How do you use a grinder with a cutting wheel?

How to Use an Angle Grinder with a Cutting Wheel
Every second of operation with a rotating cutting wheel is a calculated risk. Proper placement, leakage protection, avoiding direct exposure, and applying even pressure – these seemingly simple operations contain life-saving protocols. From installing protective covers to power-off maintenance, every detail forms the foundation of safety. Master these 11 ironclad rules to ensure metal cutting remains free from accidents.
I. Operational Guidelines for Cutting Wheels
- Secure Placement
- Position the angle grinder on stable ground away from flammable materials
- Connect to a leakage protection device for electrical safety
- Proper Installation
- Install cutting wheel according to specifications
- Verify smooth rotation before operation
- Workpiece Security
- Ensure clamping devices are reliable to prevent material slippage
- Prevent potential injuries from loose workpieces
- Cutting Technique
- Maintain consistent pressure during operation
- Always stand to the side, never in line with the cutting wheel
- Post-Operation Care
- Clean machine surface and work area promptly
- Implement rain protection measures for outdoor use
II. Critical Safety Precautions
- Pre-Operation Checks
- Verify switch integrity and proper grounding
- Ensure all safety features are functional
- Operational Control
- Apply steady pressure to the control handle
- Avoid excessive force that may cause wheel fracture
- Regular Maintenance
- Inspect clamping mechanism monthly
- Verify integrity of handwheels, screws, and nuts
- Structural Integrity
- Confirm lever strength and rigidity
- Ensure free wheel movement when fully assembled
- Mechanical Components
- Maintain smooth rotation of pivot shafts
- Secure all lever assemblies firmly
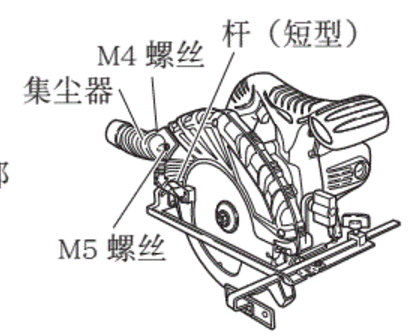
III. Wheel Replacement Protocol
- Preparation
- Disconnect power completely
- Verify new wheel specifications match requirements
- Removal Process
- Carefully detach fastening screws
- Dispose of old wheels properly
- Installation
- Align new wheel correctly
- Secure fasteners to specified torque
- Testing
- Conduct trial run after installation
- Monitor for vibrations or abnormal sounds
IV. Maintenance Procedures
- Cleaning
- Regularly remove surface deposits
- Prevent uneven wear patterns
- Inspection
- Check for cracks or damage weekly
- Replace compromised wheels immediately
- Operational Limits
- Avoid exceeding rated capacity
- Prevent equipment damage
- Storage
- Maintain dry storage conditions
- Prevent moisture absorption or thermal deformation
Conclusion
The cutting wheel serves as an essential tool for processing various hard materials, with selection depending on specific material properties. By adhering to these operational, safety, and maintenance guidelines, users can optimize cutting performance while extending equipment service life. Remember that proper technique and vigilance transform powerful tools into safe, productive assets.