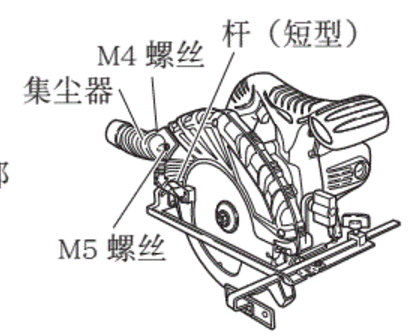
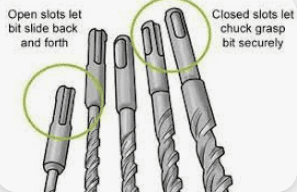
Can you use sDs drill bits for metal?

yes. SDS drill bits can used for metal.
What is the Official Term for Hammer Drill Bits?
1. Official Terminology
The official term for hammer drill bits is “rotary impact drill bit”, also known as an “SDS drill bit”.
- SDS stands for “Steck-Schlitz-System” (Insert-Slot-System), referring to its quick-connect shank design.
2. Key Features
Hammer drill bits combine rotary and impact action for faster, more efficient drilling. Compared to traditional bits, they offer:
- High Efficiency: Rapid material penetration for quicker drilling.
- Durability: Made from special alloys to withstand high heat, pressure, and wear.
- Stability: SDS shank ensures a secure connection with the drill, minimizing wobble.
3. Applications
Widely used in construction, manufacturing, and repairs for drilling into:
- Concrete, stone (e.g., wall anchors, pipe installations)
- Metal (e.g., sheet metal fabrication)
- Wood (e.g., furniture assembly)
SDS Drill Bit Shank Sizes
SDS bits come in two standard shank sizes:
- 6.4mm: Fits 6.4mm metal bits / 12.8mm wood bits (limited applications).
- 9.5mm: Drills 9.5mm holes in metal or 19mm in wood.
- With hole saws, can bore up to 76mm.
- Often includes hammer mode for concrete and reverse function for screw removal.
How to Choose the Right Drill Bit?
Selecting a drill bit depends on the material and project requirements. Key factors:
Selection Criteria
| Factor | Options |
|---|---|
| Material | HSS, Carbide, Cobalt, Diamond |
| Shank Type | Straight, Hex, SDS, Morse Taper |
| Bit Type | Twist, Step, Masonry, Spade |
| Coating | Titanium, Black Oxide, etc. |
Material-Specific Bits
| Material | Recommended Bit Type | Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Wood | Spade, Auger, Brad-point | Sharp tip prevents splintering |
| Metal | HSS, Cobalt, Carbide | Use low RPM + cutting oil |
| Masonry | Carbide-tipped SDS/Hex | Hammer mode required |
| Tile/Glass | Spear-point, Diamond core | Drill slowly with water cooling |
Drill Bit Types & Specifications
Masonry Bits
| Shank | Material | Quality (★) | Edges | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smooth/SDS+ | Carbide | ★★★★ | 2-4 | Concrete, stone, brick |
| SDS Max | Carbide | ★★★★★★ | 4+ | Reinforced concrete |
Metal Bits
| Material | Coating | Quality | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSS | None | ★★ | Soft metals (aluminum) |
| HSS-Co | Cobalt | ★★★★★ | Stainless steel, hard alloys |
| Carbide | TiN | ★★★★★★ | High-precision machining |
Wood Bits
- Spade: Flat head for rough holes.
- Auger: Spiral flute for deep, clean holes.
- Brad-point: Sharp tip for precision.
Tile/Glass Bits
- Diamond core: Wet drilling for ceramics.
- Spear-point: Low-speed penetration.
Geometric Shapes for Specialized Drilling
- Twist Bits (HSS): General-purpose for wood/metal/plastic.
- Step Bits: Adjustable diameter for thin metals.
- Countersink Bits: Combine drilling + chamfering.
Pro Tips for Wall Drilling
- Small holes (6–10mm): Use triangular-shank bits (more stable than round shanks).
- Multipurpose bits: Combine masonry/metal/tile drilling (e.g., eccentric/triangular bits).
- Avoid old round-shank masonry bits—prone to slipping.
Final Note: Always match the bit to your drill’s chuck type (SDS, hex, etc.) and operating mode (hammer vs. rotary).
Summary:
- Hammer drill bits = Rotary impact bits (SDS).
- Choose by material, shank type, and geometry.
- Prioritize carbide for masonry, HSS/cobalt for metal.
- Triangular shanks > round shanks for stability.
This guide ensures you drill smarter, not harder! 🔧
To read more about ev charging station or packing technology in China.