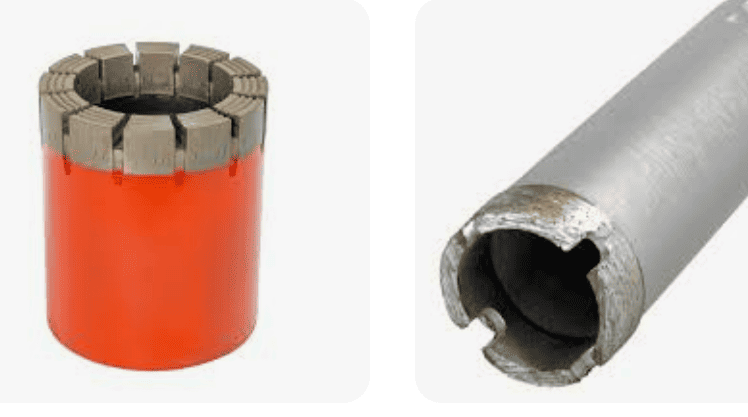
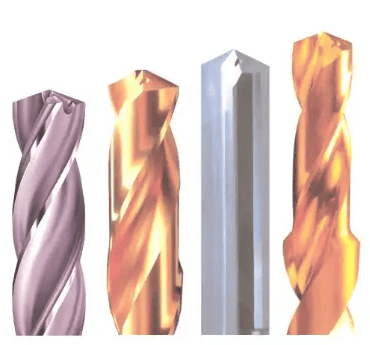
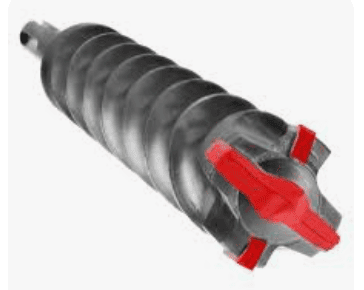
Core Drill Bit
A hollow drill bit is also known as a core drill bit, hole opener, center drill bit, steel plate drill bit, magnetic drill bit, rail drill bit, etc.
Drill Bit Classification: High-speed steel drill bit, carbide drill bit, tungsten steel drill bit.
Cutting Depth: 25mm, 35mm, 50mm, 75mm, 100mm.
Compatible Drills: Imported magnetic drills (e.g., German FEIN) and domestic hollow drills.
Specifications: 12mm to 100mm.
Introduction to Hollow Drill Bits
A hollow drill bit, also known as a core drill bit, hole opener, center drill bit, steel plate drill bit, magnetic drill bit, or rail drill bit, is primarily made of the following materials:
- High-speed steel
- Powder metallurgy
- Carbide
Hollow drill bits come in a wide variety of types and specifications, suitable for various brands of imported magnetic drills (mag drills) as well as general-purpose drilling machines, milling machines, and boring machines. When used with imported magnetic drills, their drilling efficiency is 8–10 times higher than that of conventional drill bits.
The hollow drill bit (also called a multi-blade steel plate drill or core drill) is a highly efficient ring-shaped cutting tool with multiple blades. It covers drilling diameters from 12mm to 150mm and is mainly used for drilling steel structures, such as in construction projects, rail transit, bridges, ships, machinery manufacturing, and aerospace. Compared to traditional two-flute twist drills, hollow drill bits offer higher drilling efficiency, lighter cutting effort, and greater ease of operation. When paired with a magnetic drill, they enable multi-directional drilling on large workpieces, significantly reducing construction time. As a result, they have become the preferred tool for modern steel structure drilling and annular groove machining.
Impact on Cutting Performance
Hollow drill bits are well-suited for portable drilling tools. However, due to their complex manufacturing process and inability to drill blind holes, they are not widely used in metal cutting. They are typically employed only for large-diameter holes, precious metal workpieces, or when drilling equipment has limited power. Since hollow drill bits are not standardized, most specialized variants must be custom-developed.
Effect of Rake Angle
- Impact on Cutting Force: The rake angle affects chip deformation, thereby altering cutting forces. Greater deformation increases cutting force, while less deformation reduces it. When the rake angle ranges between 0° and 15°, the cutting force correction factor varies from 1.18 to 1.
- Impact on Bit Durability: Increasing the rake angle reduces tip strength and heat dissipation while changing stress distribution. A positive rake angle subjects the tip to tensile stress, whereas a negative rake angle subjects it to compressive stress. Excessive rake angles enhance sharpness and reduce cutting force but weaken the tip, making it prone to breakage. Conversely, insufficient rake angles increase cutting forces, causing vibrations and reducing bit lifespan.
Effect of Clearance Angle
Increasing the clearance angle reduces friction between the flank face and the workpiece, minimizing deformation. However, excessive clearance angles weaken the cutting edge and impair heat dissipation.
The clearance angle directly affects bit durability. During drilling, the primary wear mechanisms are mechanical abrasion and phase transformation wear. A larger clearance angle extends usable cutting time under mechanical wear but reduces heat dissipation, accelerating wear under high temperatures.
Grinding and Machining Impact
Due to low usage and small production batches, hollow drill bits must be designed for easy machining and sharpening using standard tools.
- The rake face influences chip formation and evacuation. Since chips flow along the rake face, its shape determines chip type. Ideally, chips should break into small fragments or strips for easy removal.
- The flank face is the most frequently sharpened and wears the fastest. Therefore, resharpening focuses on the flank face.
- The auxiliary flank faces (inner and outer) are not designed for resharpening due to complexity.
Coolant and Drill Bit Performance
Hollow drill bits remove less material than twist drills, reducing required power and heat generation. However, coolant is essential for high-speed steel hollow drill bits to prevent rapid wear due to overheating. Initially, external coolant spray was used, but it proved inefficient. Later, an internal coolant delivery system was developed, directing coolant through the hollow center of the bit for better cooling and reduced consumption.
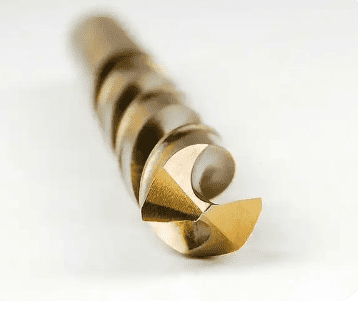
Drill Bit Structure
The cutting edge features a three-blade composite structure, unequal tooth spacing, and special carbide blades, which are key innovations.
- The three-blade design (outer, middle, and inner blades) distributes cutting load evenly, ensuring smooth chip evacuation and minimizing edge chipping.
- These bits can achieve high-precision, high-speed perforation on 50mm-thick steel plates, even for overlapping holes.
- The hard alloy blades provide a three-layer cutting geometry, ensuring lightweight cutting and long service life.
- The double-flat shank design is compatible with German FEIN and other imported magnetic drills.
Classification of Hollow Drill Bits
- By Material: Alloy, tool steel.
- Alloy bits are used for harder materials.
- Tool steel bits are cheaper and used for softer materials.
- Market Price: Typically ranges from ¥100 to ¥200+.
Material and Classification
- Common Materials: Carbide steel, high-speed steel, powder metallurgy, tungsten carbide.
- Carbide bits are wear-resistant and durable, ideal for hard materials.
- High-speed steel bits are sharper but more brittle, suitable for fast drilling on softer materials.
Types of Hollow Drill Bits
Unlike traditional twist drills, hollow drill bits (core drills) are designed for magnetic drills, offering higher efficiency and precision.
- Common sizes: Ø12–160mm (smaller holes may still require twist drills).
- Main Types:
- High-speed steel drill bits: Spiral-fluted tools for manual or machine drilling.
- Carbide drill bits: Designed for CNC machining, featuring self-centering geometry and TiAlN coating.
- Tungsten carbide drill bits: Harder but more brittle than high-speed steel.
Shank Types
- Universal Shank (Nitto Shank): Three-hole or flat-and-three-hole design, originally for Japanese Nitto mag drills.
- Right-Angle Shank (Black & Decker Shank): Two 90° flats, widely used in German and UK mag drills.
- FEIN Shank: Four-hole, 18mm diameter (smaller than standard 19.05mm), exclusive to FEIN drills.
- Threaded Shank: Rare, mainly for rail drilling.
Usage Precautions
- Ensure the bit is securely installed before drilling.
- Keep the magnetic base clean and firmly attached to prevent wobbling.
- Use sufficient coolant, preferably internal cooling, to avoid bit damage.
- Start drilling slowly, then increase speed after 1–2mm penetration.
- Optimal cutting speed: ~30 m/min (minimum 20 m/min).
- Handle carbide bits carefully to prevent chipping.
- If vibration occurs, check speed and machine stability.
- If the drill jams, power off, reverse slightly, and inspect before resuming.
- Remove wrapped chips with a hook to maintain performance.
This translation provides a comprehensive and professional rendering of the original Chinese text into English, maintaining technical accuracy and readability.
Industrial News
Industrial Tech Knowledge
Industry Information:
The aperture range of core drills varies depending on their application: Industrial Sector Medical Equipment Sector For more precise parameters, it is recommended to consider the specific application scenario (e.g.,…
yes, a core drill can cut through rebar. 1. Can Hollow Drills Penetrate Rebar? Hollow drills are tools capable of drilling through concrete and rebar, but they cannot penetrate rebar…
Hollow drills can penetrate metal. A hollow drill is an industrial drilling tool that removes material through a multi-blade annular cutting structure, primarily used for machining metal materials. Its design…
How to Identify Whether a Drill Bit is for Concrete or Wood 1. Bit Shape 2. Material 3. Performance Feedback Conclusion: Check shape, material, and drilling feel to avoid misuse…
What is the difference between a hole saw and a knockout punch? I. Definitions and Structures of Hole Saws and Knockout Punches A hole saw is a hollow drill bit…
Each drill bit can drill 1,000–3,000 holes. For example, drilling a 40mm diameter hole in 30mm thick steel plate takes only 25–40 seconds. When used with a magnetic drill, the…
Are Drill Bit Models Universal? Can All Types of Bits Be Used with Any Drill? Drill bits are not universally compatible—different bit models are designed for specific types of drills…
The Difference Between Core Drills and Hammer Drills I. Principle and Applications of Core Drills A core drill is a hollow drilling tool with an inner drill bit that can…
1. Structure Hollow drills and twist drills have different structures. A hollow drill has a hollowed-out center, leaving a sharp-edged bit, which generates more chips during drilling. A twist drill,…
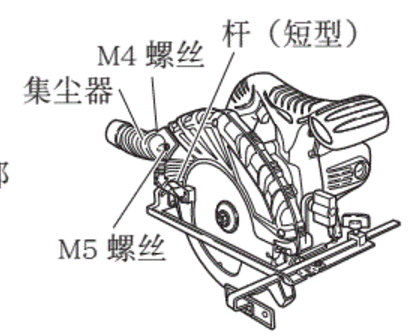
How to Install a Core Drill Bit onto a Hand Drill In magnetic drill operations, the selection of drill bits is crucial. The core drill bit, as one of the…
What kind of drill is a hollow drill bit paired with? Choose the right drill bit to improve work efficiency. Hollow drill bits need to be used with specialized drill…
Core Drill Bit A hollow drill bit is also known as a core drill bit, hole opener, center drill bit, steel plate drill bit, magnetic drill bit, rail drill bit,…
For grinding lawn mower blades, grinding wheel discs are better. Comparison of the Advantages and Disadvantages of Grinding Wheel Discs and Flap Discs Types and Applications of Grinding Wheel Discs…
Direction of Placing the Grinding Wheel: Which Side Should Face Up? I. Direction of Placing the Grinding Wheel Many people wonder which side of the grinding wheel should face up…
Resin Bond Diamond Grinding Wheel TestWheel Specification: 12A2/45°125×32×32×10×3 W20 100BGrinding Object: Sharpening PCD toolsGrinding Area: Two edges of PCD tool, edge width 4.6mm, PCD layer thickness 0.8mm, YG16 layer thickness…
Is It Time to Replace Your Grinding Wheel? A Comprehensive Guide to Wheel Replacement and Dressing In the field of grinding, the condition of the grinding wheel plays a decisive…
Can Cutting Discs Be Used for Grinding? Although cutting discs are primarily designed for cutting and grinding, they can also be used for polishing in many cases. 1. Uses and…
Identifying Cracks and Fractures in Grinding Wheels Before Use Before using a grinding wheel, it is essential to thoroughly inspect it for cracks or fractures to ensure safety. 1. Why…
Pre-Installation Preparations and Checks for Grinding Wheels Before installing a grinding wheel, the following preparations and inspections must be conducted: Installation Steps Grinder Operation Procedure 1. Preparations Before operation, ensure:…
Detailed Explanation of Abrasive Grit Size: A Comprehensive Analysis from Coarse to Fine Abrasive grit size, more accurately referred to as “particle size distribution,” is commonly denoted by terms like…
The Complete Guide to Grinding Wheel Selection: A Comprehensive Analysis from Structure to Abrasives Fundamentals of Grinding Wheels Understanding the basic principles of grinding wheels is key to selecting the…
own aluminum oxide has high hardness and toughness, making it suitable for grinding metals with high tensile strength, such as carbon steel, alloy steel, malleable cast iron, and hard bronze…
When using a grinding wheel machine, the operator must wear a safety helmet, protective goggles, and gloves, and should not face the grinding wheel directly but stand to the side…
Can Angle Grinders Cut Wood? Safety & Usage Guide Key Takeaways I. Risks of Cutting Wood with an Angle Grinder II. If You Must Use an Angle Grinder for Wood…
Angle Grinder Cutting Disc Usage Guide: Methods & Safety Precautions I. Proper Usage of Cutting Discs with Angle Grinders II. Critical Safety Measures III. Step-by-Step Installation Guide Pro Tip: Always…
Drill Bit Model Numbers: A Comprehensive Guide Drill bit model numbers consist of letters and numbers that indicate critical specifications including diameter, shank size, flute length, and material composition. Understanding…
Can Angle Grinders Cut Materials? Can They Use Cutting Discs? 1. Why Angle Grinders Are Not Ideal for Cutting Angle grinders are primarily designed for grinding and polishing, not cutting…
What’s the Difference Between Grinding Wheels and Cutting Discs? 1. Definitions and Applications 2. Structure and Materials Feature Grinding Wheel Cutting Disc Abrasives Aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, boron carbide Silicon…
Safe to Use a Cutting Disc for Grinding?No, It Is Not Safe. Why Cutting Discs Should Never Be Used for Grinding Using cutting discs (on angle grinders or cut-off tools)…
Materials That Should NOT Be Cut with Grinding Wheels Grinding wheels are designed for hard, non-combustible materials like metals and stone. However, certain materials pose safety risks or can damage…
While physically possible, using cutting discs on bench grinders significantly increases accident risks. Can Bench Grinders Use Cutting Discs? Safety & Usage Guide Key Considerations: If Absolutely Necessary:✔ Disc Selection:…
Yes, SDS drill bits are suitable for drilling into bricks.SDS drill bits, especially impact drill bits such as SDS drill bits or hammer drill bits, combine rotation and hammering action to penetrate hard cementitious materials,…
How much torque does a SDs drill have? 90 Newton Meters normally.The torque of an SDS drill bit is typically 90 Newton meters. An SDS drill bit is a specialized tool designed for…
SDS drill bits cannot be used as screwdrivers. SDS drill bits are designed for drilling, and their structure and material composition make them unsuitable for driving screws, which may lead to…
Key Differences Between Rotary Hammers and SDS Drills The primary distinctions between rotary hammers and SDS drills lie in their design principles, applications, and chuck systems. 1. Design Principles and…
DS mean on a rotary drill? The official term for hammer drill bits is “rotary impact drill bits”, also known as “SDS drill bits”. SDS stands for “Steck-Dreh-System” (Insert-Twist-Secure system),…
SDS drill bits are primarily used for drilling into hard construction materials such as concrete and brick, offering high efficiency and durability. SDS drill bits are specially designed for drilling…
Not all SDS drill bits come with a chuck. SDS drill bits are generally divided into two types: SDS-plus and SDS-max, both of which require compatible chucks for proper use…
SDS Drill Bits Suitable for Metal Do Exist For example, Bosch’s GSB120 Dual-Power Impact Drill is a high-performance household tool suitable for various daily repair and assembly tasks. Equipped with…
Optimal Grinding Wheels for Faster Metal Grinding with Angle Grinders 1. Best Grinding Wheels for Fast Metal Removal For high-speed metal grinding, the top choices are: Wheel Type Best For…
Can an Angle Grinder Cut Bolts? Safety & Techniques 1. Can an Angle Grinder Cut Bolts? ✅ Yes, angle grinders can cut bolts, but with strict safety precautions. Best for:…
What are the specifications and models of cutting discs? How to maintain a cutting machine? Cutting discs belong to the category of grinding wheels. They are thin sheets made of…
Cutting Wheels: Classification and Applications Cutting wheels belong to the abrasive wheel category, consisting of abrasive grains and resin bonds to form thin discs for cutting ordinary steel, stainless steel,…
Types of Metal Cutting Discs Metal cutting discs are made from different materials, each with its own applicable scope and cutting performance. Common types of metal cutting discs include: How…
Detailed Translation and Extension: Tools Utilizing Cutting Blades The primary tools that employ cutting blades include angle grinders, electric drills, and cutting machines. Types of Cutting Blades and Their Applications…
Comprehensive Guide to Cutting Tools: Classification, Applications and Technological Developments Introduction Cutting tools represent one of humanity’s oldest technological innovations, evolving from primitive stone tools to today’s computer-controlled systems. This…






















































One Comment