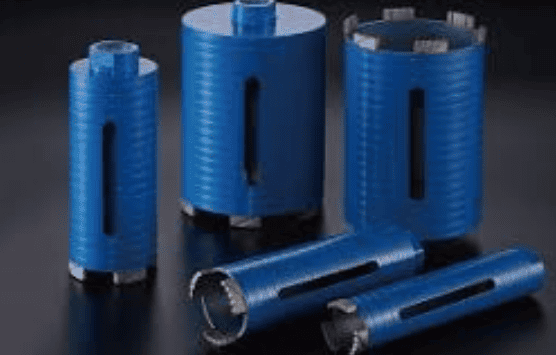
What is the difference between a rotary drill and a core drill?
The main differences between rotary drills and hollow drills lie in their applications, structures, and working principles.
Differences in Applicability
Hollow drill bits (straight drilling) and rotary drills also differ in their scope of application.
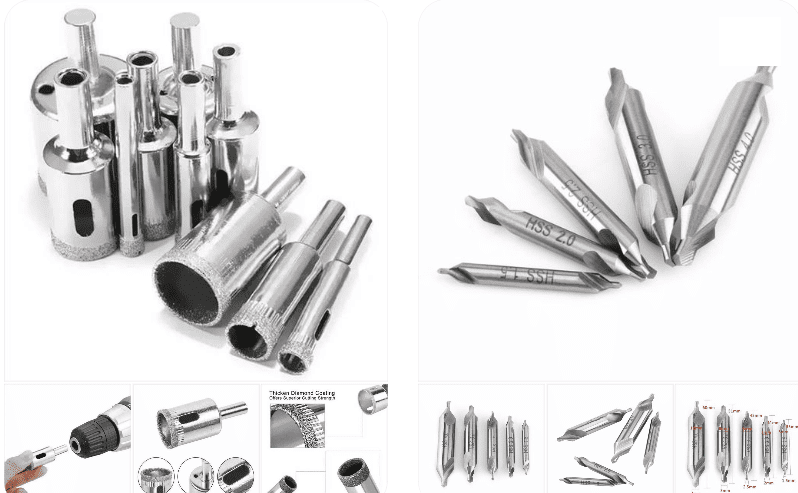
Hollow drill bits are suitable for processing harder metals, as well as materials like ceramics, marble, and glass, with particularly notable effectiveness on glass. Rotary drills, on the other hand, are more versatile and are used for drilling materials such as wood, iron, aluminum, and copper.
Applications
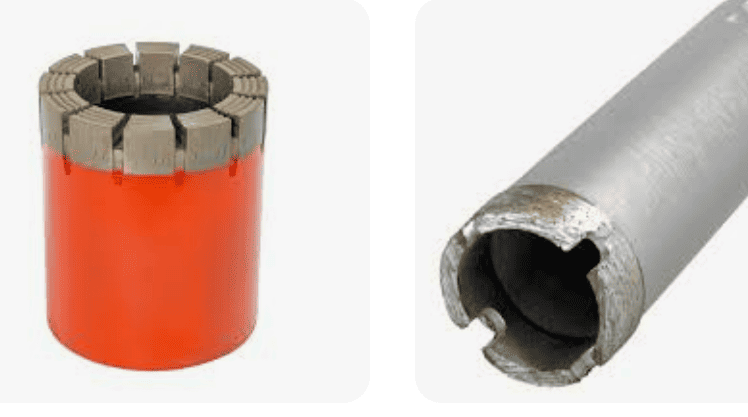
- Hollow Drills: Primarily used in steel structure engineering, rail transit, shipbuilding, and other fields for machining holes with diameters ranging from 12–150 mm and depths of 25–200 mm. Their core technology lies in a multi-blade annular cutting structure, where the outer, middle, and inner blades share the cutting load, and a spring ejector rod facilitates automatic chip removal.
- Rotary Drills: Mainly used for drilling into rock layers in open-pit coal mines, suitable for rocks with a strength index of f ≤ 6, and can also handle harder interbedded rocks with f = 7–11. Their working principle involves increasing rotational torque and axial pressure to drive the twist drill’s rotation and feed motion for rock cutting.
Structures
- Hollow Drills: Feature a modular blade structure, with each set of cutting edges bearing only one-third of the total workload. The outer blade is responsible for annular groove positioning, the middle blade handles the main cutting load, and the inner blade completes core severing and chip removal. Their chip flute design uses uneven tooth spacing to reduce resonance probability, working in tandem with a spring ejector rod for automatic chip removal.
- Rotary Drills: Are characterized by a hydraulic crawler telescopic chassis, self-lifting foldable drill mast, and telescopic drill tools, offering lightweight and comfortable operation. Dual main and auxiliary winches adapt to various construction site conditions.
Working Principles
Hollow drill bits (straight drilling) and rotary drills differ significantly in their working principles.
Hollow drill bits have a hollow structure with a cylindrical hole in the center. During operation, the bit rotates and advances, pulling material out through the central hole to form the bore. They are suitable for perforation and cutting tasks. Hollow drills employ a multi-blade annular cutting mechanism for material removal, with each set of blades having a distinct role, and a spring ejector rod ensures automatic chip disposal. The core technology lies in the three-blade combined cutter head, where the outer, middle, and inner blades share the cutting load.
Rotary drills, in contrast, are conventional solid-structure bits. During use, the bit rotates while axial force is applied, generating rotational friction against the material. The resulting heat and friction remove material to create the hole. Rotary drills function by increasing rotational torque and axial pressure to drive the twist drill’s rotation and feed motion for rock cutting. In soft strata, they achieve faster drilling speeds but produce more cuttings, requiring high-volume drilling to ensure thorough bottom-hole cleaning and effective bit cooling.
Usage Precautions
Whether using hollow drill bits or rotary drills, the following points should be noted:
- Select the appropriate drill bit based on the material’s hardness.
- Pay attention to the bit’s angle and size, as different dimensions and angles suit different bore diameters and drilling angles.
- Maintain bit cooling and lubrication to reduce heat and friction, enhancing bit lifespan and efficiency.
- Gradually increase the feed speed during drilling to avoid excessive force that could damage the bit.
Conclusion
Through this introduction, we can understand the differences between hollow drill bits and rotary drills in terms of working principles, applicability, structural designs, and usage precautions. In practice, selecting the right drilling tool based on specific processing requirements ensures more efficient and precise results.
You may also interest in: 11kw ev charger; Granule filling machine; plastic roll packing.