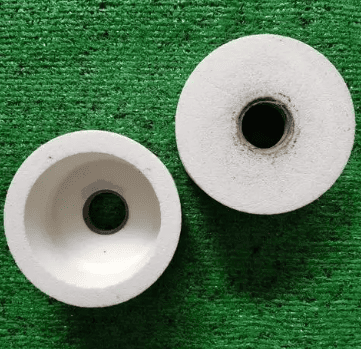
What is the difference between pink and GREY grinding stones?

The main differences between pink grinding wheels and gray grinding wheels lie in their composition and applicable scenarios.
Pink grinding wheels are typically chromium corundum grinding wheels, primarily composed of alumina raw material mixed with chromium oxide and titanium oxide, dissolved, crushed, and then refined with emery. Chromium corundum grinding wheels are suitable for grinding workpieces with high surface finish requirements, such as cutting tools, measuring instruments, gauges, and threads.
Gray grinding wheels, on the other hand, are mixed abrasive grinding wheels, mainly composed of alumina raw material mixed with zirconium oxide, dissolved, crushed, and refined with emery. Mixed abrasive grinding wheels are typically gray and are suitable for grinding a variety of materials, offering good versatility and durability.
Applicable Scenarios and Performance Characteristics
- Pink grinding wheels: Suitable for high-precision machining, such as cutting tools, measuring instruments, and gauges, where high surface quality is required. Due to their high hardness, they are ideal for fine machining and applications demanding superior surface finishes.
- Gray grinding wheels: Suitable for grinding various materials, offering excellent versatility and durability. The mixed abrasive design ensures outstanding performance when working with materials of different hardness levels, making them ideal for situations requiring frequent wheel changes.
Color Classification of Jinze Abrasive Grinding Wheels
I. Introduction to Jinze Abrasive Grinding Wheels
Jinze abrasive grinding wheels are a common type of grinding tool widely used in industries such as metal processing, glass manufacturing, and ceramic production. They consist of abrasives, binders, and pores, and perform grinding operations on workpieces through high-speed rotation. The color of a grinding wheel is often related to its performance, application, and abrasive type. Therefore, understanding the color classification of Jinze abrasive grinding wheels is crucial for selecting and using them correctly.
II. Color Classification of Jinze Abrasive Grinding Wheels
- Gray grinding wheels
The most common type, typically made of silicon carbide or alumina abrasives. Gray grinding wheels have moderate hardness and are suitable for general metal grinding, such as rough and fine grinding of steel, copper, and aluminum. They offer high cost-effectiveness and are the preferred choice for many manufacturers. - White grinding wheels
Primarily made of white corundum (alumina), these wheels exhibit high hardness and wear resistance. They are suitable for harder materials, such as hardened steel and tool steel. White grinding wheels have strong cutting power but are relatively expensive, often used in high-precision and high-efficiency grinding applications. - Pink grinding wheels
Typically made of chromium corundum abrasives, these wheels offer high toughness and impact resistance. They are suitable for grinding difficult-to-machine materials like stainless steel and high-speed steel. Pink grinding wheels are less prone to chipping during use and have good durability, though they are relatively expensive. - Green grinding wheels
Mainly composed of green silicon carbide abrasives, these wheels are suitable for processing hard and brittle materials, such as ceramics, glass, and cemented carbide. Green grinding wheels have high hardness and excellent wear resistance, though their cutting power is relatively weaker. They hold significant value in specific applications, such as ceramic tool manufacturing. - Black grinding wheels
Typically made of black silicon carbide abrasives, these wheels are suitable for processing cast iron and non-ferrous metals. Black grinding wheels offer moderate cutting power and hardness, with high cost-effectiveness, making them widely used in various types of grinders and grinding machines.
III. Relationship Between Jinze Abrasive Grinding Wheel Color and Performance
The color of Jinze abrasive grinding wheels primarily reflects their abrasive type and performance characteristics. Wheels of different colors exhibit varying hardness, wear resistance, cutting power, and application ranges. Therefore, when selecting a Jinze abrasive grinding wheel, factors such as the material being processed, required precision, and efficiency should be considered to choose the most suitable type.
IV. Conclusion
Understanding the color classification of Jinze abrasive grinding wheels is essential for their correct selection and use. In practical applications, choosing the appropriate wheel color based on processing requirements can achieve optimal results. Additionally, the color classification provides a convenient identification method, helping to improve work efficiency and processing quality.
Decoding Grinding Wheel Colors: Key Factors Affecting Grinding Performance
Grinding wheels are indispensable tools for cutting hard and brittle materials, composed of sharp abrasives and binders. During high-speed rotation, they self-sharpen, generating new cutting surfaces. Their vibrant colors stem from the types of abrasives (e.g., green silicon carbide, pink chromium corundum), binders (resin, metal, ceramic), and dyes. However, color serves only as an auxiliary identifier for model differentiation; actual performance depends on a comprehensive evaluation of five key characteristics, including abrasive hardness and binder strength.
Basics of Grinding Wheels
Definition and Function of Grinding Wheels
What exactly is a grinding wheel, this indispensable tool for cutting hard and brittle materials? It is a circular object formed by bonding coarse abrasive particles with a compound, featuring hard, sharp, and heat-resistant abrasive grains on its outer edge. As the wheel rotates at high speed, these grains act like sharp blades, cutting and grinding the workpiece surface. Notably, grinding wheels continuously self-sharpen during use, creating new abrasive gaps (pores), a characteristic that underscores their critical role in industrial applications.
The Mystery of Grinding Wheel Colors
If you are familiar with grinding wheels, you may have noticed an intriguing phenomenon: their “complexions” vary widely, with different models displaying a dazzling array of colors. This naturally raises questions: What causes this diversity in grinding wheel colors? What differences exist among wheels of different colors? Does color play a significant role in selecting a grinding wheel? Next, we will explore the secrets behind grinding wheel colors.
Factors Influencing Grinding Wheel Colors
Role of Abrasives and Binders
The primary factors affecting grinding wheel colors include abrasives, binders, and pores, with abrasives and binders having the most significant impact. Dyes also play a crucial role.
As the core material of a grinding wheel, abrasives perform the primary cutting tasks. Thus, they must possess sharpness, high hardness, excellent heat resistance, and appropriate toughness. The market offers a wide variety of abrasives, such as corundum, silicon carbide, diamond, and cubic boron nitride. These abrasives inherently exhibit distinct colors—for example, silicon carbide may appear green or black, white corundum is pure white, chromium corundum has a pink hue, and ceramic corundum abrasives typically display a light blue tone.
To firmly bond hard abrasive particles into a specific shape, binders play a vital role. Their functions are twofold: First, binders connect dispersed abrasives to form a grinding tool with certain strength and hardness. Second, the binder’s holding strength (bonding degree) directly affects key performance metrics such as grinding efficiency, self-sharpening ability, and shape retention. Common binder materials in grinding tools include resin, metal, and ceramic, whose colors also influence the wheel’s appearance—for instance, golden-yellow resin binders lend a brownish tint to the wheel.
Use of Dyes
If the colors we observe in grinding wheels—such as orange, deep yellow, or pink—are not inherent to their components, they are achieved through external means: dyes. Grinding wheel manufacturers often add dyes during the mixing process to impart these vivid colors, facilitating the differentiation of wheels by model or application.
Grinding Wheel Colors and Grinding Performance
Complexity of Color Influence
The impact of color on grinding performance is relatively complex and requires discussion from multiple perspectives. First, the type of abrasive is a key factor—for example, alumina-based abrasives are particularly suitable for grinding ferrous metals. However, it is important to note that grinding wheels may contain multiple abrasives, and their colors may not be uniform but rather a composite reflection of mixed abrasive properties. Second, binder characteristics also influence grinding performance. Additionally, dyes in grinding wheels primarily serve to distinguish models and do not directly affect grinding performance.
Comprehensive Evaluation of Grinding Performance
In summary, while grinding wheel color can provide a preliminary indication of abrasive type, this method is not always accurate. The wheel’s appearance is influenced by multiple factors, including abrasive type, binder properties, dye presence, and pore density. Therefore, to accurately assess grinding performance, it is best to conduct a comprehensive evaluation based on the wheel’s five key characteristics: abrasive material, grain size, binder properties, and hardness.