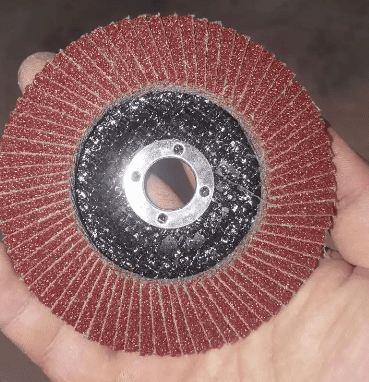
Direction of Placing the Grinding Wheel: Which Side Should Face Up?
I. Direction of Placing the Grinding Wheel
Many people wonder which side of the grinding wheel should face up when placing it. In fact, there is no definitive answer, but we can determine it based on the following points:
- Flat Surface Up: In most cases, placing the flatter side up ensures smoother operation and better grinding performance.
- Label Side Up: If the wheel has markings or serial numbers, place that side up for easy identification during use.
- Dense Grit Side Up: To prevent burning or scorching, place the side with denser, smoother grit facing up, reducing the risk of scorching.
In general, placing the flatter, less gritty side up yields better results.
When using a grinding wheel, the abrasive side usually faces outward for direct contact with the workpiece. Our in-store flap discs, with a diameter of 300mm, thickness of 25mm, and grit size of 240#, are ideal for grinding, polishing, and rust removal. These imported products are reliable, moderately weighted, and easy to operate. Designed for optimized grinding performance, they can handle various grinding tasks effortlessly.
II. Tips for Using Grinding Wheels
Beyond placement, proper usage ensures safety and efficiency. Here are key points to note:
- Inspect Before Use: Check for damage or cracks; replace if any defects are found.
- Test Run: Spin the wheel for a few minutes to allow self-balancing before formal use.
- Control Speed: Do not exceed 50% of the rated speed.
- Avoid Overuse: Prevent excessive wear and grit shedding; replace worn wheels promptly.
- Wear Protective Gear: Use workwear, goggles, etc., to ensure safety.
- Correct Handling: Avoid lateral pressure to prevent cracking or bursting.
Proper, safe, and correct use of grinding wheels enhances efficiency, ensures personal safety, and prolongs equipment life. We hope this guide helps.
How to Properly Store Grinding Wheels: Flat or Vertical?
I. Discussion on Storage Methods
Grinding wheels can be stored flat (horizontally) or vertically. The choice depends on workspace and needs.
II. Pros and Cons of Flat Storage
- Pros: Higher stability, less rolling risk, even weight distribution, reduced breakage risk.
- Cons: Occupies more space, unsuitable for cramped areas.
III. Considerations for Vertical Storage
- Pros: Saves space, ideal for limited areas.
- Cons: Lower stability; requires extra securing to prevent falls. Long-term vertical storage may cause structural damage.
IV. Practical Recommendations
- Surface Grinders: Flat storage is preferred for stability and longevity.
- Space Constraints: Vertical storage is acceptable if securely fixed.
V. Conclusion
Flat storage is generally safer, while vertical storage suits tight spaces. Prioritize stability, safety, and space efficiency for optimal grinding operations.
Standards and Specifications for Grinder Installation
Today, we’ll discuss grinder installation standards:
- Orientation: The grinder’s opening should face a wall, not walkways or nearby personnel.
- Shielding: If near equipment or walkways, install a 1.8m metal screen 1–1.5m from the opening.
- Environment: Avoid corrosive or flammable areas; keep the floor dry.
- Lighting: Ensure adequate illumination.
Grinders are high-speed, versatile tools often used manually. Poor maintenance or unsafe practices can lead to accidents.
Key Points for Grinding Wheel Installation and Adjustment
As technology advances, precision requirements for parts (e.g., hydraulic valves, laser mirrors, optical components) drive ultra-precision grinding, lapping, and polishing.
Installation Notes:
- Pre-Installation Check: Suspend the wheel and tap it; a clear, ringing sound indicates integrity.
- Flange Mounting: Use identical flanges (min. 1/3 wheel diameter; 2/3 if unguarded).
- Cushioning: Place rubber or felt gaskets between wheel and flange for even pressure.
- Test Run: Operate idle for ≥5 minutes before use.
- New Wheel Check: Inspect for cracks; perform static balancing before and after installation.
Balancing Procedure:
- Tools: Balance stand, mandrel, balance weights, level.
- Mark Heavy Point (A) and opposite point (B).
- Add Weights (C, D, E) while keeping A/B positions fixed.
- Adjust Weights: If positions shift, rebalance by adjusting D/E.
- Rotate 90°: Repeat until stable in all orientations (test 6–8 positions).
Balanced wheels ensure safe, efficient operation.
Industrial News
Industrial Tech Knowledge
Industry Information:
The aperture range of core drills varies depending on their application: Industrial Sector Medical Equipment Sector For more precise parameters, it is recommended to consider the specific application scenario (e.g.,…
yes, a core drill can cut through rebar. 1. Can Hollow Drills Penetrate Rebar? Hollow drills are tools capable of drilling through concrete and rebar, but they cannot penetrate rebar…
Hollow drills can penetrate metal. A hollow drill is an industrial drilling tool that removes material through a multi-blade annular cutting structure, primarily used for machining metal materials. Its design…
How to Identify Whether a Drill Bit is for Concrete or Wood 1. Bit Shape 2. Material 3. Performance Feedback Conclusion: Check shape, material, and drilling feel to avoid misuse…
What is the difference between a hole saw and a knockout punch? I. Definitions and Structures of Hole Saws and Knockout Punches A hole saw is a hollow drill bit…
Each drill bit can drill 1,000–3,000 holes. For example, drilling a 40mm diameter hole in 30mm thick steel plate takes only 25–40 seconds. When used with a magnetic drill, the…
Are Drill Bit Models Universal? Can All Types of Bits Be Used with Any Drill? Drill bits are not universally compatible—different bit models are designed for specific types of drills…
The Difference Between Core Drills and Hammer Drills I. Principle and Applications of Core Drills A core drill is a hollow drilling tool with an inner drill bit that can…
1. Structure Hollow drills and twist drills have different structures. A hollow drill has a hollowed-out center, leaving a sharp-edged bit, which generates more chips during drilling. A twist drill,…
How to Install a Core Drill Bit onto a Hand Drill In magnetic drill operations, the selection of drill bits is crucial. The core drill bit, as one of the…
What kind of drill is a hollow drill bit paired with? Choose the right drill bit to improve work efficiency. Hollow drill bits need to be used with specialized drill…
Core Drill Bit A hollow drill bit is also known as a core drill bit, hole opener, center drill bit, steel plate drill bit, magnetic drill bit, rail drill bit,…
For grinding lawn mower blades, grinding wheel discs are better. Comparison of the Advantages and Disadvantages of Grinding Wheel Discs and Flap Discs Types and Applications of Grinding Wheel Discs…
Resin Bond Diamond Grinding Wheel TestWheel Specification: 12A2/45°125×32×32×10×3 W20 100BGrinding Object: Sharpening PCD toolsGrinding Area: Two edges of PCD tool, edge width 4.6mm, PCD layer thickness 0.8mm, YG16 layer thickness…
Is It Time to Replace Your Grinding Wheel? A Comprehensive Guide to Wheel Replacement and Dressing In the field of grinding, the condition of the grinding wheel plays a decisive…
Can Cutting Discs Be Used for Grinding? Although cutting discs are primarily designed for cutting and grinding, they can also be used for polishing in many cases. 1. Uses and…
Identifying Cracks and Fractures in Grinding Wheels Before Use Before using a grinding wheel, it is essential to thoroughly inspect it for cracks or fractures to ensure safety. 1. Why…
Pre-Installation Preparations and Checks for Grinding Wheels Before installing a grinding wheel, the following preparations and inspections must be conducted: Installation Steps Grinder Operation Procedure 1. Preparations Before operation, ensure:…
Detailed Explanation of Abrasive Grit Size: A Comprehensive Analysis from Coarse to Fine Abrasive grit size, more accurately referred to as “particle size distribution,” is commonly denoted by terms like…
The Complete Guide to Grinding Wheel Selection: A Comprehensive Analysis from Structure to Abrasives Fundamentals of Grinding Wheels Understanding the basic principles of grinding wheels is key to selecting the…
own aluminum oxide has high hardness and toughness, making it suitable for grinding metals with high tensile strength, such as carbon steel, alloy steel, malleable cast iron, and hard bronze…
When using a grinding wheel machine, the operator must wear a safety helmet, protective goggles, and gloves, and should not face the grinding wheel directly but stand to the side…
Can Angle Grinders Cut Wood? Safety & Usage Guide Key Takeaways I. Risks of Cutting Wood with an Angle Grinder II. If You Must Use an Angle Grinder for Wood…
Angle Grinder Cutting Disc Usage Guide: Methods & Safety Precautions I. Proper Usage of Cutting Discs with Angle Grinders II. Critical Safety Measures III. Step-by-Step Installation Guide Pro Tip: Always…
Drill Bit Model Numbers: A Comprehensive Guide Drill bit model numbers consist of letters and numbers that indicate critical specifications including diameter, shank size, flute length, and material composition. Understanding…
Can Angle Grinders Cut Materials? Can They Use Cutting Discs? 1. Why Angle Grinders Are Not Ideal for Cutting Angle grinders are primarily designed for grinding and polishing, not cutting…
What’s the Difference Between Grinding Wheels and Cutting Discs? 1. Definitions and Applications 2. Structure and Materials Feature Grinding Wheel Cutting Disc Abrasives Aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, boron carbide Silicon…
Safe to Use a Cutting Disc for Grinding?No, It Is Not Safe. Why Cutting Discs Should Never Be Used for Grinding Using cutting discs (on angle grinders or cut-off tools)…
Materials That Should NOT Be Cut with Grinding Wheels Grinding wheels are designed for hard, non-combustible materials like metals and stone. However, certain materials pose safety risks or can damage…
While physically possible, using cutting discs on bench grinders significantly increases accident risks. Can Bench Grinders Use Cutting Discs? Safety & Usage Guide Key Considerations: If Absolutely Necessary:✔ Disc Selection:…
Yes, SDS drill bits are suitable for drilling into bricks.SDS drill bits, especially impact drill bits such as SDS drill bits or hammer drill bits, combine rotation and hammering action to penetrate hard cementitious materials,…
How much torque does a SDs drill have? 90 Newton Meters normally.The torque of an SDS drill bit is typically 90 Newton meters. An SDS drill bit is a specialized tool designed for…
SDS drill bits cannot be used as screwdrivers. SDS drill bits are designed for drilling, and their structure and material composition make them unsuitable for driving screws, which may lead to…
Key Differences Between Rotary Hammers and SDS Drills The primary distinctions between rotary hammers and SDS drills lie in their design principles, applications, and chuck systems. 1. Design Principles and…
DS mean on a rotary drill? The official term for hammer drill bits is “rotary impact drill bits”, also known as “SDS drill bits”. SDS stands for “Steck-Dreh-System” (Insert-Twist-Secure system),…
SDS drill bits are primarily used for drilling into hard construction materials such as concrete and brick, offering high efficiency and durability. SDS drill bits are specially designed for drilling…
Not all SDS drill bits come with a chuck. SDS drill bits are generally divided into two types: SDS-plus and SDS-max, both of which require compatible chucks for proper use…
SDS Drill Bits Suitable for Metal Do Exist For example, Bosch’s GSB120 Dual-Power Impact Drill is a high-performance household tool suitable for various daily repair and assembly tasks. Equipped with…
Optimal Grinding Wheels for Faster Metal Grinding with Angle Grinders 1. Best Grinding Wheels for Fast Metal Removal For high-speed metal grinding, the top choices are: Wheel Type Best For…
Can an Angle Grinder Cut Bolts? Safety & Techniques 1. Can an Angle Grinder Cut Bolts? ✅ Yes, angle grinders can cut bolts, but with strict safety precautions. Best for:…
What are the specifications and models of cutting discs? How to maintain a cutting machine? Cutting discs belong to the category of grinding wheels. They are thin sheets made of…
Cutting Wheels: Classification and Applications Cutting wheels belong to the abrasive wheel category, consisting of abrasive grains and resin bonds to form thin discs for cutting ordinary steel, stainless steel,…
Types of Metal Cutting Discs Metal cutting discs are made from different materials, each with its own applicable scope and cutting performance. Common types of metal cutting discs include: How…
Detailed Translation and Extension: Tools Utilizing Cutting Blades The primary tools that employ cutting blades include angle grinders, electric drills, and cutting machines. Types of Cutting Blades and Their Applications…
Comprehensive Guide to Cutting Tools: Classification, Applications and Technological Developments Introduction Cutting tools represent one of humanity’s oldest technological innovations, evolving from primitive stone tools to today’s computer-controlled systems. This…
Comprehensive Guide to Cutting Disc Replacement Standards: Technical Specifications and Best Practices 1. Precise Wear Measurement Standards The industry-standard replacement threshold is reached when: 2. Advanced Wear Detection Methods 2.1…